Online legal research
Westlaw Canada: Trusted legal content at your fingertips
Complete online legal research confidently by leveraging award-winning content, essential tools, unmatched editorial enhancements, and world-renowned research support
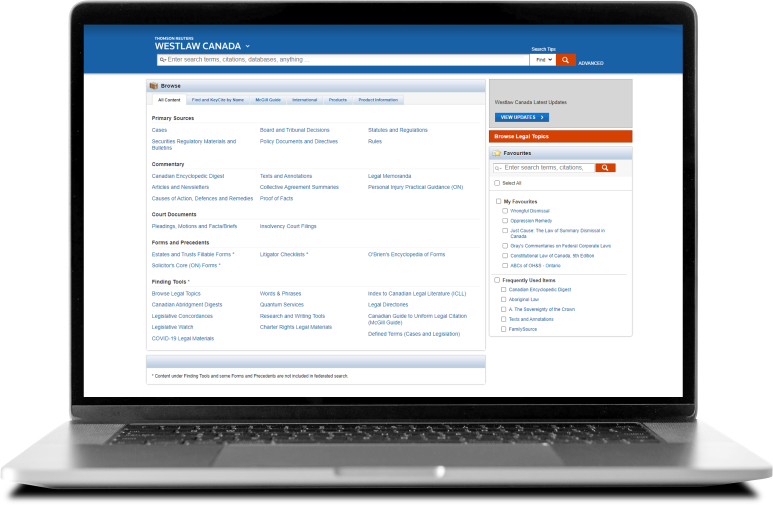
Unparalleled legal content and essential online research tools
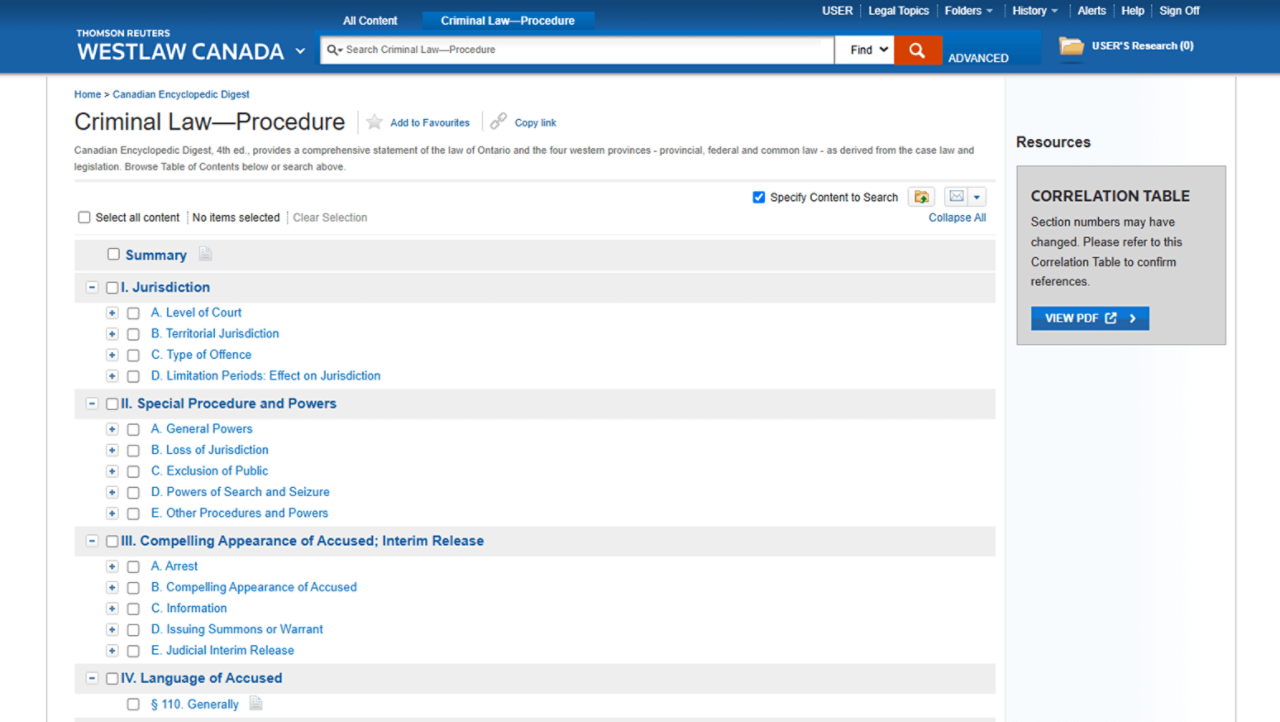
Rely on expert content for your legal research
Access the most up-to-date and organized collections of case law, statutes, and regulations, regularly vetted by a team of expert lawyer-editors to ensure they meet rigorous editorial standards. This content includes The Canadian Encyclopedic Digest (CED), the Canadian Abridgment, and the Index to Canadian Legal Literature (ICLL).
Explore more features
Have questions?
Contact a representative
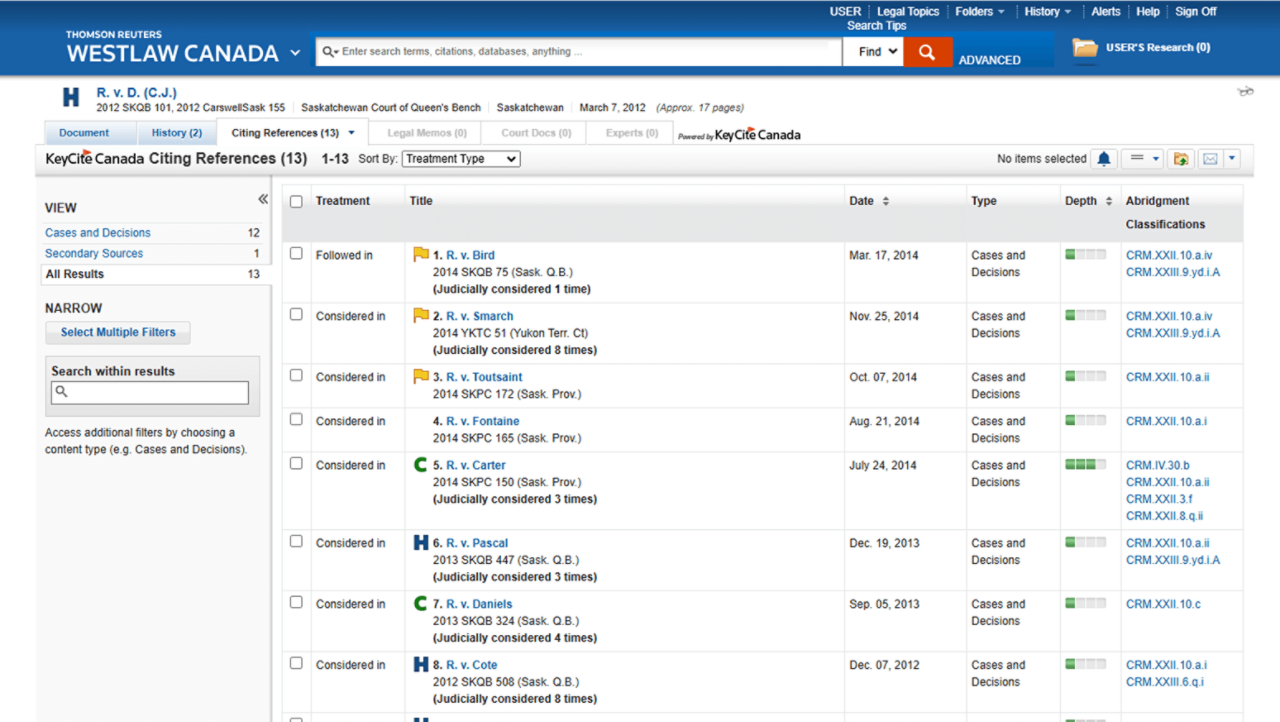
Ensure you are citing good law with KeyCite Canada
Quickly verify whether a case, statute, or other legal authority is still good law. KeyCite Canada makes it possible for legal professionals to rely on the most accurate, current information when encountering invalid or overruled points of law.
Explore more features
Have questions?
Contact a representative
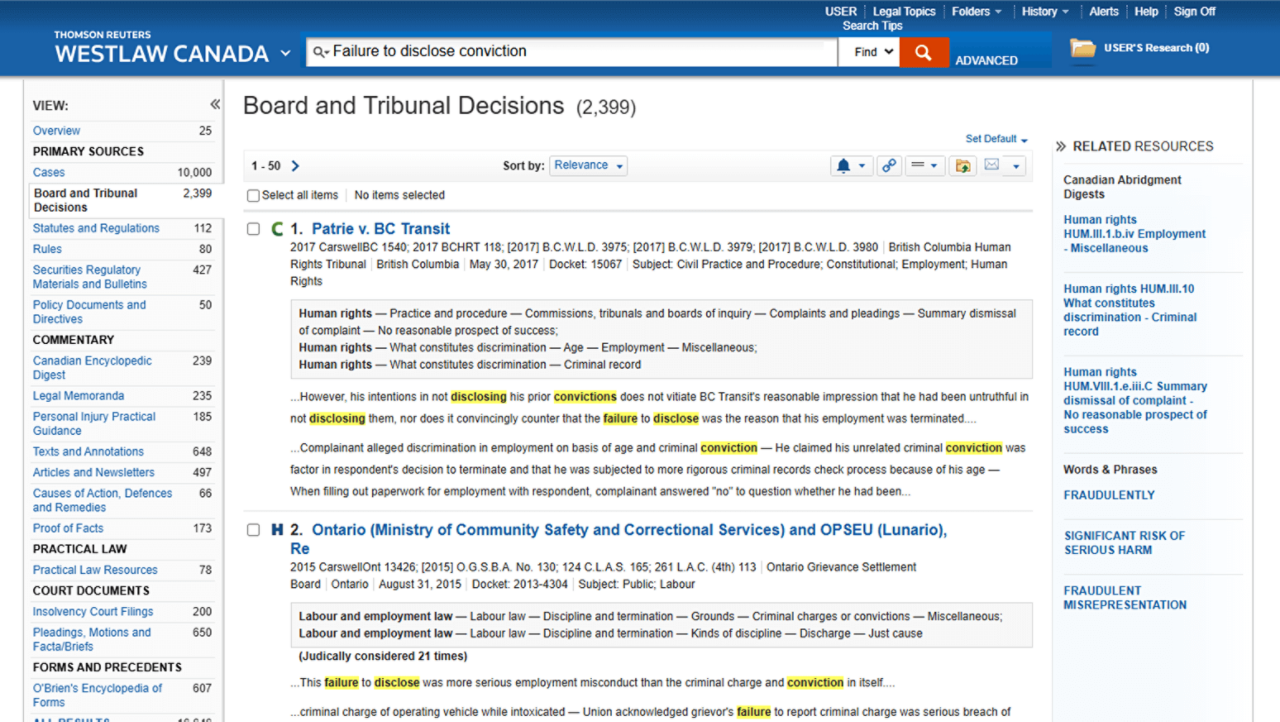
Find the information you need faster with Westlaw Canada Search
Deliver the best results quickly and with more confidence with Canada’s most advanced legal search engine. You can use either natural language or Boolean connectors to find the exact content you need using this intuitive and easy-to-use search functionality.
Explore more features
Have questions?
Contact a representative
The value of Westlaw Canada
Improved accuracy in less time
Quickly find the answers you need — grounded in expertly written content — and stop second-guessing your sources, potentially saving hours per week on legal research tasks.
Maintenance of legal knowledge
Monitor changes to local, provincial, and national law and research the impact of pivotal legislation so you can provide effective counsel to your clients or organization.
World-renowned research support
Keep your legal research tasks on track with Westlaw Canada's industry-leading legal content paired with expert research support, helping you find what you need quickly.

Westlaw Canada contains an unparalleled library of award-winning legal content
Westlaw Canada won awards for its primary and secondary legal content in the latest Canadian Lawyer Readers’ Choice awards.
Questions about Westlaw Canada? We're here to support you.
866-609-5811
Call us or submit your email and a sales representative will contact you within one business day.
Contact us